Introduction
Read an interesting blog by @HostileCoding (can be found here) about using Google Chart with PowerCLI and thought it would be great to integrate it with webCommander. For more information about Google Chart, click here.
Configuration
First of all, Google Chart function needs to be embedded into webCmd.xsl in JavaScript format. A sample bar chart from Google is shown below:
<html> <head> <scripttype="text/javascript"src="https://www.google.com/jsapi"></script> <scripttype="text/javascript"> google.load("visualization","1",{packages:["corechart"]}); google.setOnLoadCallback(drawChart); function drawChart(){ var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable([ ['Year','Sales','Expenses'], ['2004',1000,400], ['2005',1170,460], ['2006',660,1120], ['2007',1030,540] ]); var options ={ title:'Company Performance', vAxis:{title:'Year', titleTextStyle:{color:'red'}} }; var chart =new google.visualization.BarChart(document.getElementById('chart_div')); chart.draw(data, options); } </script> </head> <body> <divid="chart_div"style="width:900px;height:500px;"></div> </body></html>
Let’s think about how to put this function into webCmd.xsl. First thing will be to define a new if statement in the result xsl template, i.e. <xsl:template name=”result”> and I called it chart, <xsl:if test=”result/chart”>. After inserting the sample above, it will look like the following (Bold & Italic represents static values):
<xsl:if test="result/chart">
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.google.com/jsapi"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load("visualization", "1", {packages:["corechart"]});
google.setOnLoadCallback(drawChart);
function drawChart(){
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable([
['Year','Sales','Expenses'],
['2004',1000,400],
['2005',1170,460],
['2006',660,1120],
['2007',1030,540]
]);
var options ={
title:'Company Performance',
vAxis:{title:'Year', titleTextStyle:{color:'red'}}
};
var chart=new google.visualization.BarChart(document.getElementById('chart_div'));
chart.draw(data, options);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chart_div" style="width: 100%; height: 500px"></div>
</body>
</xsl:if>
Now, it will be required to call it from PowerShell script. It’s quite simple:
Write-Output "<chart>" Write-Output "</chart>"
And the output will be:
Now, there are three things to think about.
- Title of the chart
- Input data
- Size of the chart
JavaScript and xsl works quite well that it is simple enough to define a JavaScript variable and value to be retrieved using xsl. Examples are shown below:
- var charttitle = ‘<xsl:value-of select=”result/chart/charttitle” />’
- var datalist = <xsl:value-of select=”result/chart/datalist” />
The name of variables can be anything you would like to use but there is one critical thing to note that variable charttitle has ” and datalist doesn’t. The reason is quite simple, charttitle is string and datalist is a hash table. The data cannot be parsed as a string.
Last thing to work on is to autosize the chart. It can be set to a static size but the problem is people have different size of monitors that might doesn’t fit in well. The following could be added in:
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function () {
$(window).resize(function(){
drawChart();
});
});
</script>
Using the above autosize function as well as two variables replacing the static values, the final version will be:
<xsl:if test="result/chart">
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.google.com/jsapi"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function () {
$(window).resize(function(){
drawChart();
});
});
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load("visualization", "1", {packages:["corechart"]});
google.setOnLoadCallback(drawChart);
function drawChart() {
var charttitle = '<xsl:value-of select="result/chart/charttitle" />'
var datalist = <xsl:value-of select="result/chart/datalist" />
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable(datalist);
var options = {
'title': charttitle
};
var chart = new google.visualization.PieChart(document.getElementById('chart_div'));
chart.draw(data, options);
}
</script>
</head>
<div id="chart_div"></div>
</xsl:if>
It is time to write up a simple PowerCLI script to load the chart function. For the PowerCLI script, I referenced @HostileCoding’s script.
$server = New-Server $ServerAddress $ServerUser $ServerPassword
$stat = "mem.usage.average"
$vm_list = Get-Cluster -Name $Cluster -Server $server.viserver -wa 0 -EA stop -ErrorVariable error_message | Get-VM | Where {$_.PowerState -eq "PoweredOn"} | Sort Name
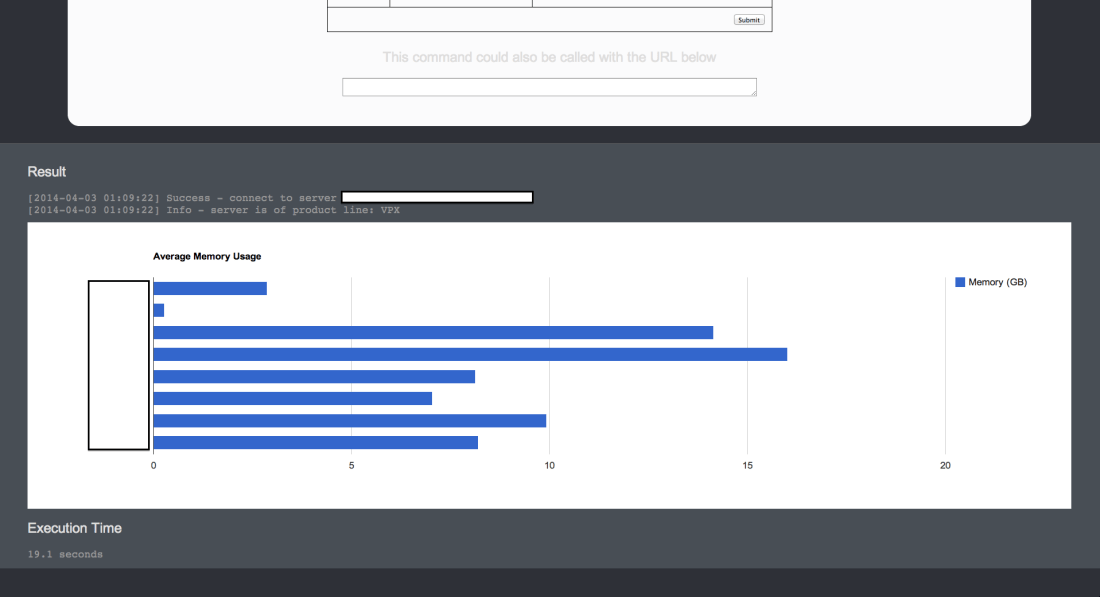
$charttitle = "Average Memory Usage"
$datalist = "[['Virtual Machine', 'Memory (GB)'],"
foreach ($vm in $vm_list) {
$value = Get-Stat -Entity $vm -Stat $stat -Start (Get-Date).AddHours(-24) -MaxSamples (10) -IntervalMins 10 | Measure-Object Value -Average
if ($value) {
$vm_name = $vm.Name
$datalist += "['$vm_name',$($value.Average)],"
}
}
$datalist = ($datalist -replace ",$") + "]"
Write-Output "<chart>"
Write-Output "<charttitle>$charttitle</charttitle>"
Write-Output "<datalist>$datalist</datalist>"
Write-Output "</chart>"
Time to run the script using webCommander! (removed the name of vCenter server and virtual machines) 😀
Thoughts
The best thing about scripting I can think of is “customisation” and “automation”. With webCommander integrated with Google Chart, it could produce more in depth reports other than just tables. Sometimes, it’s much easier to compare elements visually. Or, it will be even much better to generate a report with table and chart!
Another suggestion I can make is to utilise Google Tables instead of normal HTML table. One of the benefit of using Google Table is sorting. For example, users will able to sort a table by largest memory usage.
Hope the article is easy enough to follow and most importantly, have fun!